Generative Question Answering: Learning to Answer the Whole Question
WHY?
Discriminative question answering often overfit to datasets by catching any kinds of clue that leads to answer.
WHAT?
This paper suggests Generative Question Answering model(GQA) to generate both questions and answers given contexts. Though this paper applied the model on both QA and VQA tasks, following explanation would only focus on VQA task. The model uses Bayes’ rule to minimize the NLL of joint distribtion of questions and answers given context(images).
\mathcal{L} = -\log p(q,a|c) = -\log p(a|c) - \sum_t \log p(q_t|a, c, q_{0 ... t-1})c is encoded through pretrained convolution model(Resnet101) with 32-dimension positional encoding. Answer prior(p(a\|c)) is simply calculated with fc on image features. The likelihood of the question(p(q\|a, c)) is modeled with conditional language model. Language model(question decoder) is modeled with several blocks of residual self attentive LSTM layers and GLU on the top.
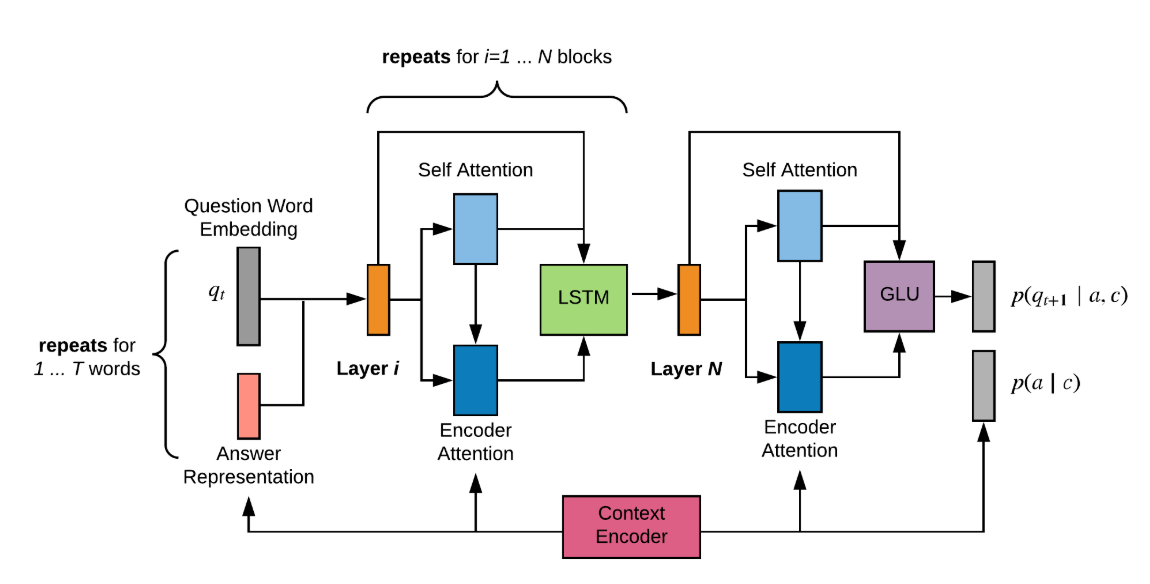
At inference time, the answer maximizing the posterior(p(q,a\|c)) is returned which requires calculation of likelihood given all possible answers.
a* = argmax_a p(q|a,c)p(a|c)So?
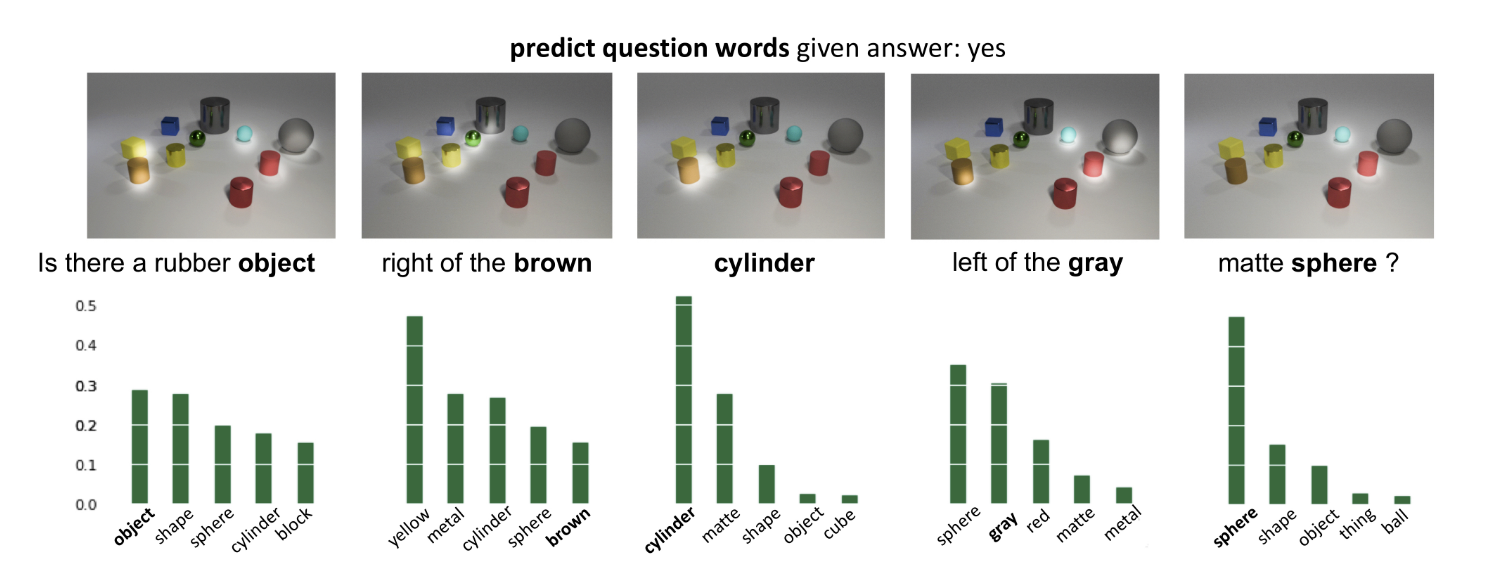
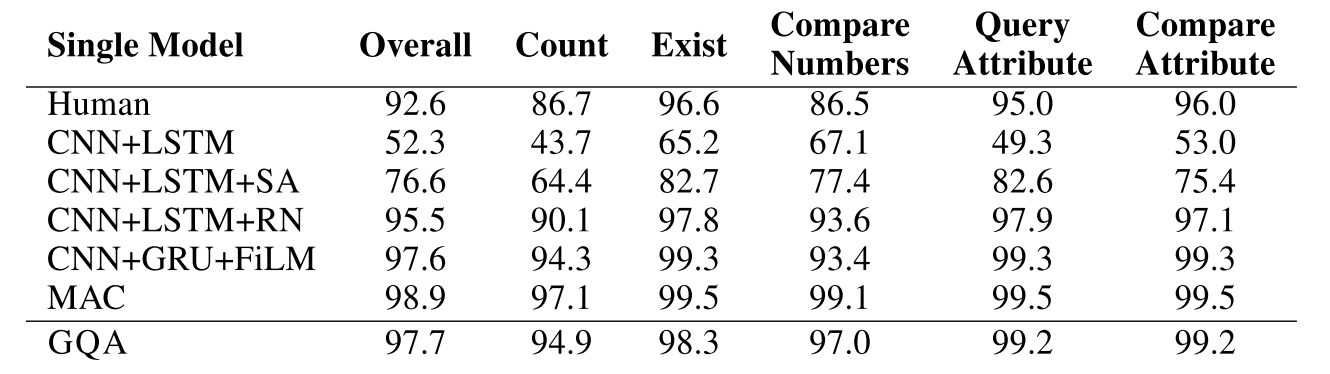
GQA showed comparable performance to other VQA models while showing interpretable attention map and word probabilities on the last layer.