Multimodal Compact Bilinear Pooling for Visual Question Answering and Visual Grounding
WHY?
Former methods used element-wise sum, product or concatenation to represent the relation of two vectors. Bilinear model(outer prodct) of two vectors is more sophisticated way of representing relation, but usually dimensionality become too big. This paper suggests multimodal compact bilinear pooling(MCB) to represent compact and sophisticated relations.
WHAT?
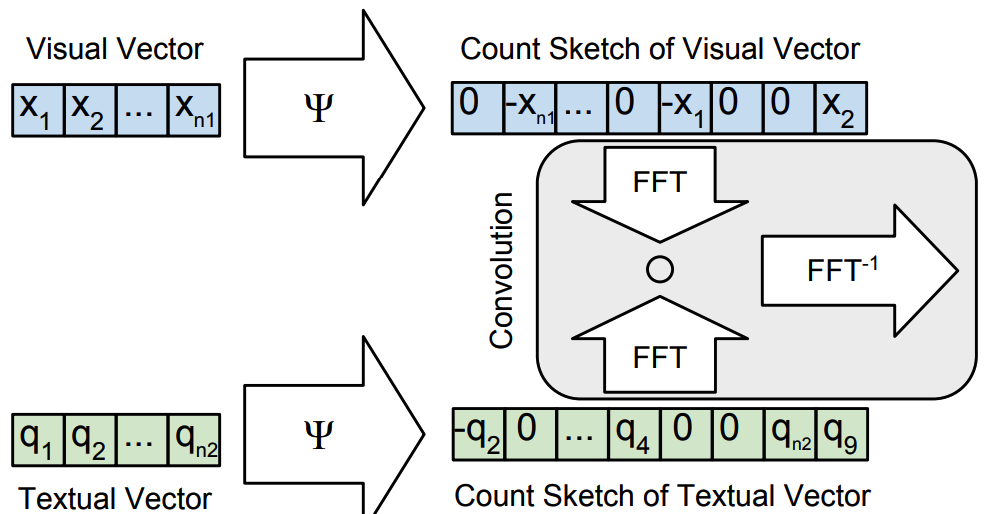
MCB utilizes Count Sketch projection function for compact encoding of vector. When projecting a vector v of size n to a vector y of size d(n > d), CS algorithm first initalize two vectors s \in \{-1, 1\}^n, and h\in {1,...,d}^n. h indicate the indexes where the values of vector v can be projected to. The algorithm is as follows.
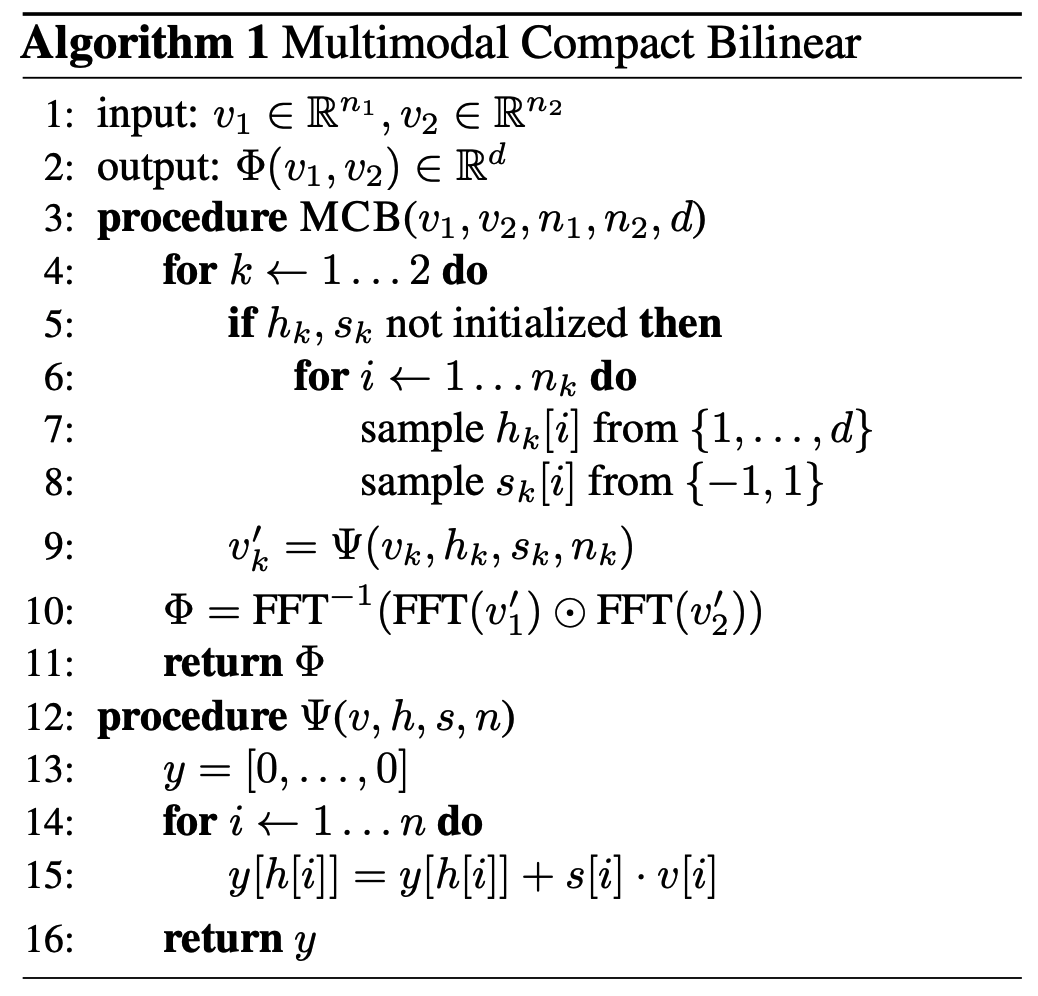
It has been proven that the Count Sketches of the outer product of two vectors can be expressed as convolution of two Count Sketches. Also, convolutino in the time domain is equivalent to element-wise product in frequency domain.
\Psi(x\otimes q, h, s) = \Psi(x, h, s) \ast \Psi(q, h, s)\\
x' \ast q' = FFT^{-1}(FFT(x')\odot FFT(q'))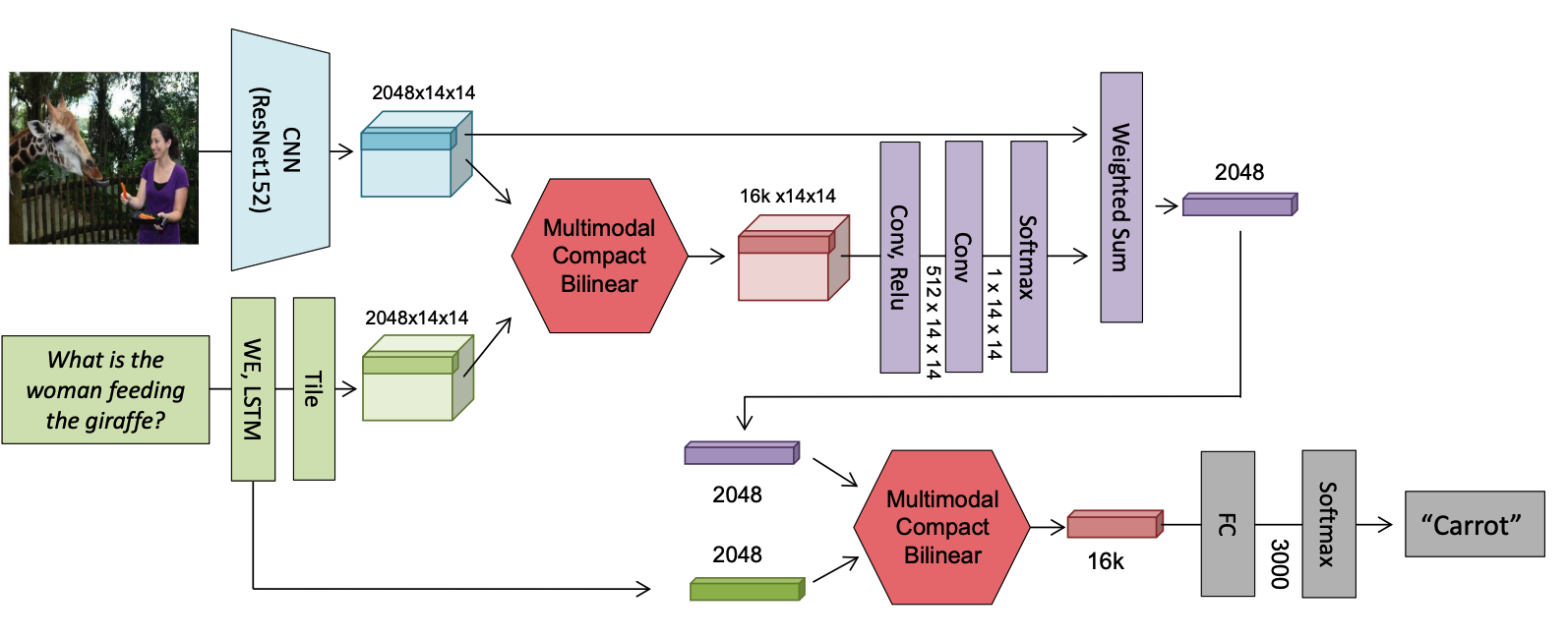
In VQA architecture, MCB pooling is used between image features and text feature to get attention weight, and attened image feature and text feature to make prediction.
So?
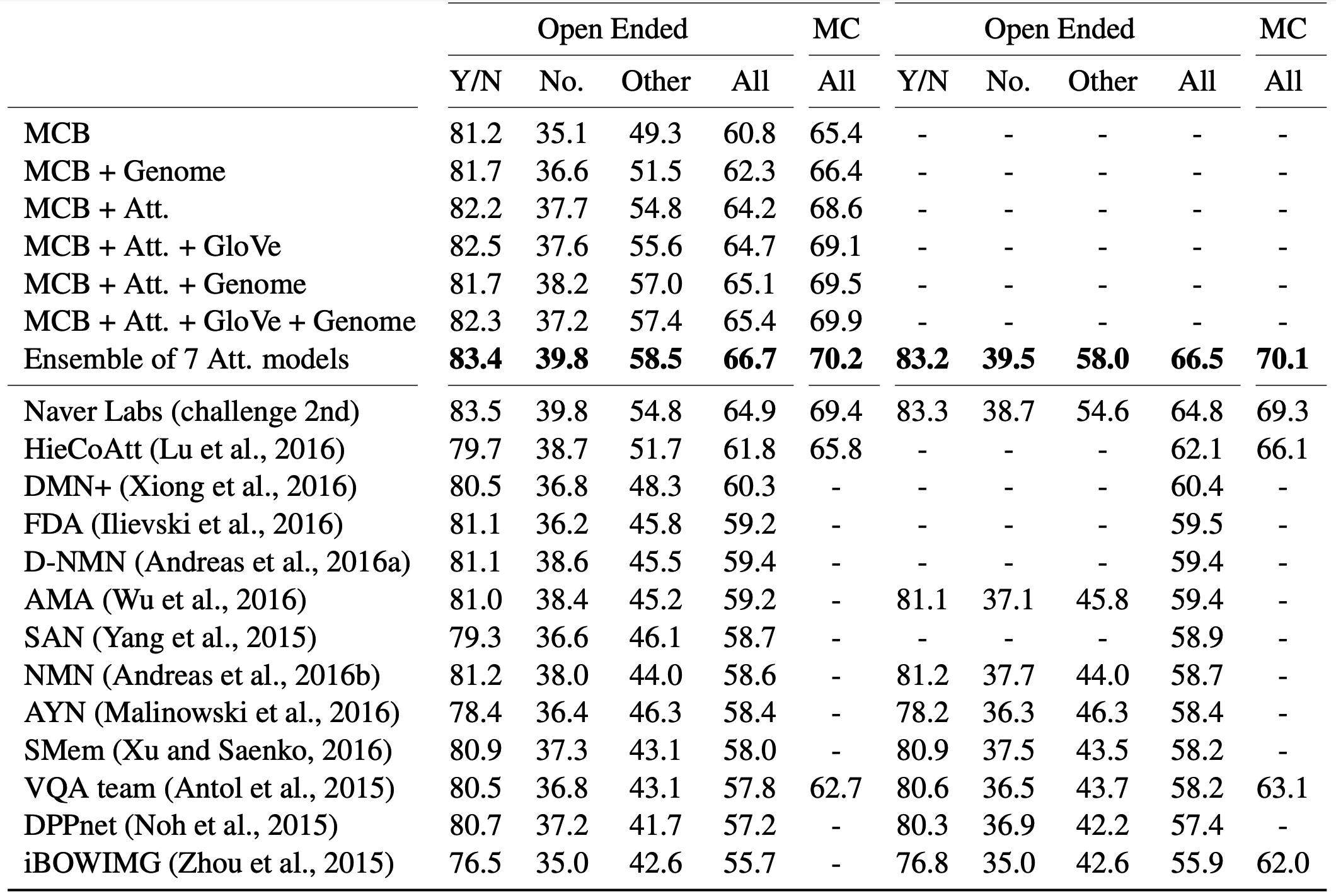
MCB achieved the good results on VQA tasks.
