U-net: Convolutional Networks for Biomedical Image Segmentation
in Studies on Deep Learning, Computer Vision
WHY?
Image segmentation requires a lot of annotated images. This paper suggests efficient training of image segmentation using data augmentation and new structure.
WHAT?
This paper suggests U-net architecture which is a modified version of fully convolutional network.
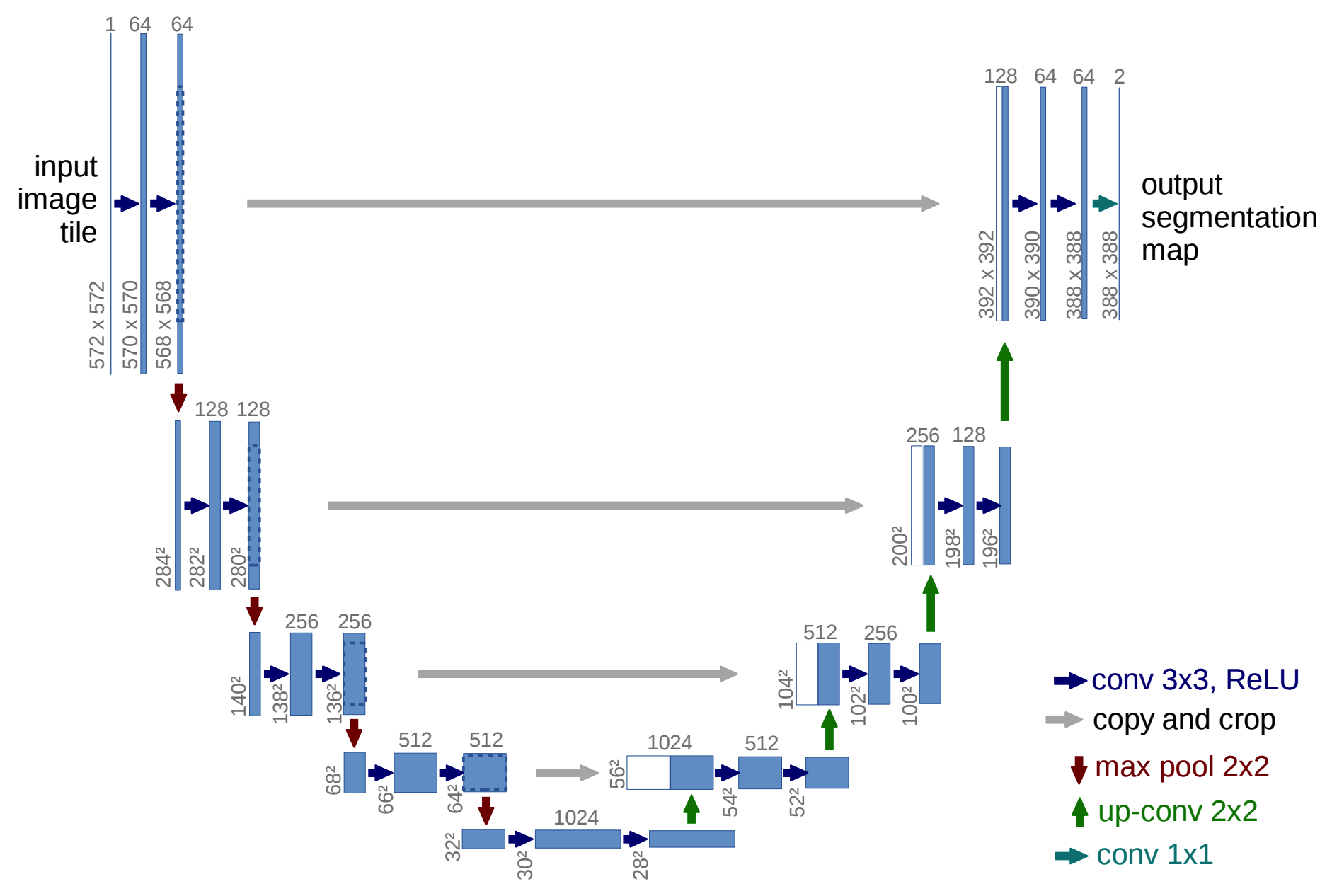
Unet consists of a contracting path and an expansive path. The contracting path is repeated application of two 3x3 convolutions, ReLU, and 2x2 max pooling with doubled channels. The expansive path is somewhat symmetric to the contracting path: two 3x3 convolutions, ReLU and 2x2 up-convolution with halved channels. After upsampling, the output of corresponding contracting layer is cropped and added to provide contextual information. These symmetric pathes form U shape structure.
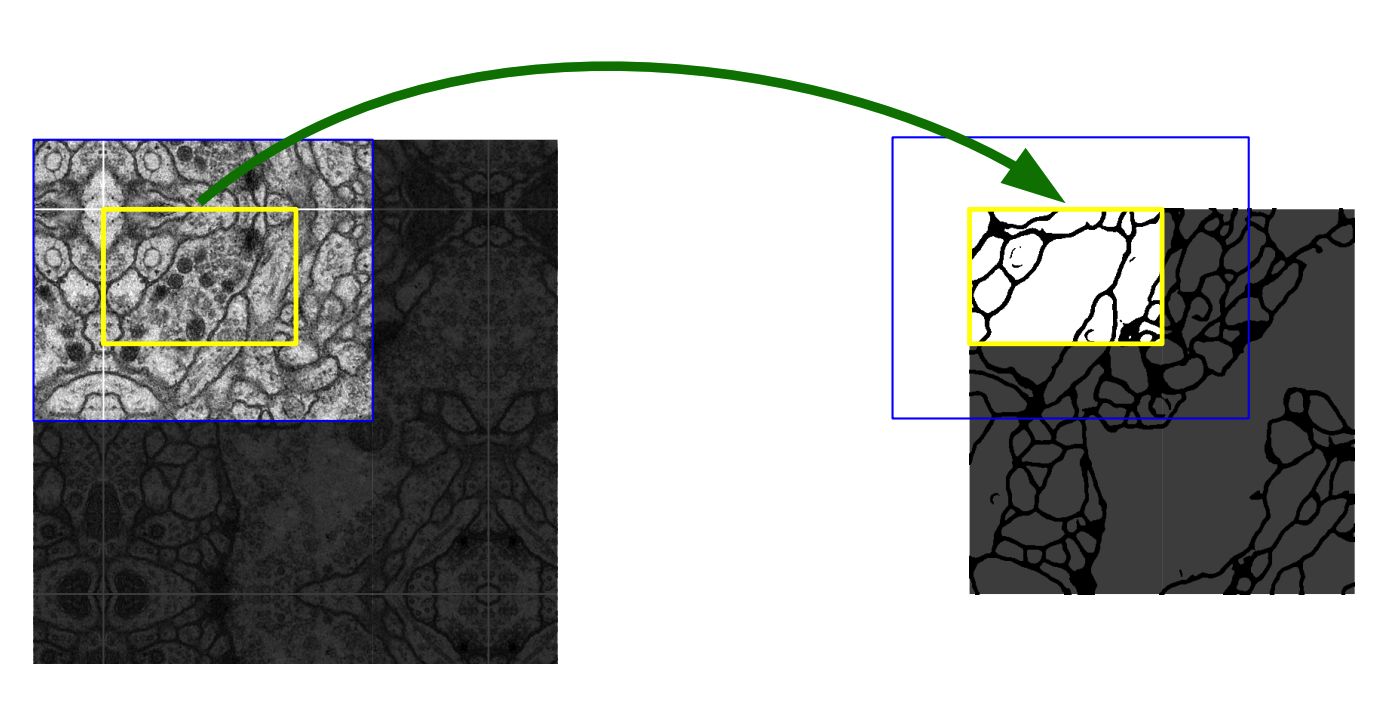
Overlap-tile strategy is used to predict segmentaion of arbitrarily large images. For efficient use of data, various kinds of data augmentations including shift and rotation invariance, elastic deformations and gray value variations is used.
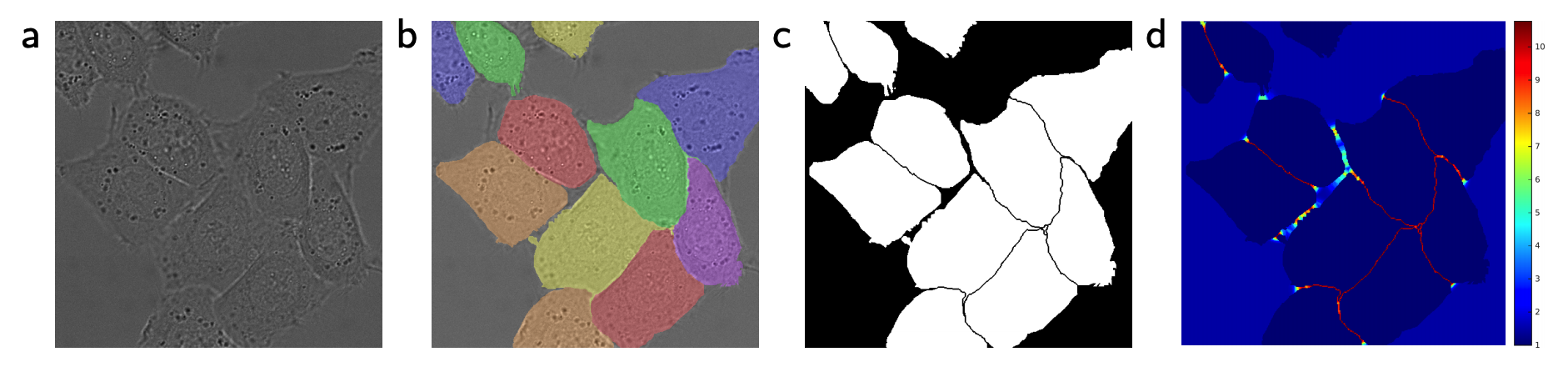
To separate the touching objects, weighted loss on the sepatation border is used.
So?
U-net achieved good results on various medical image segmentation tasks with small amount of data.
Critic
It would be better if the paper focus only on U-net structure or efficient training with data augmentation. Each contribution of the methods are not clear on the experiment results.
