Modularity Matters: Learning Invariant Relational Reasoning Tasks
in Studies on Deep Learning, Computer Vision
WHY?
Former CNN models fully activate(filly distributed features) for a single input showing poor performance on invariant relational reasoning.
WHAT?
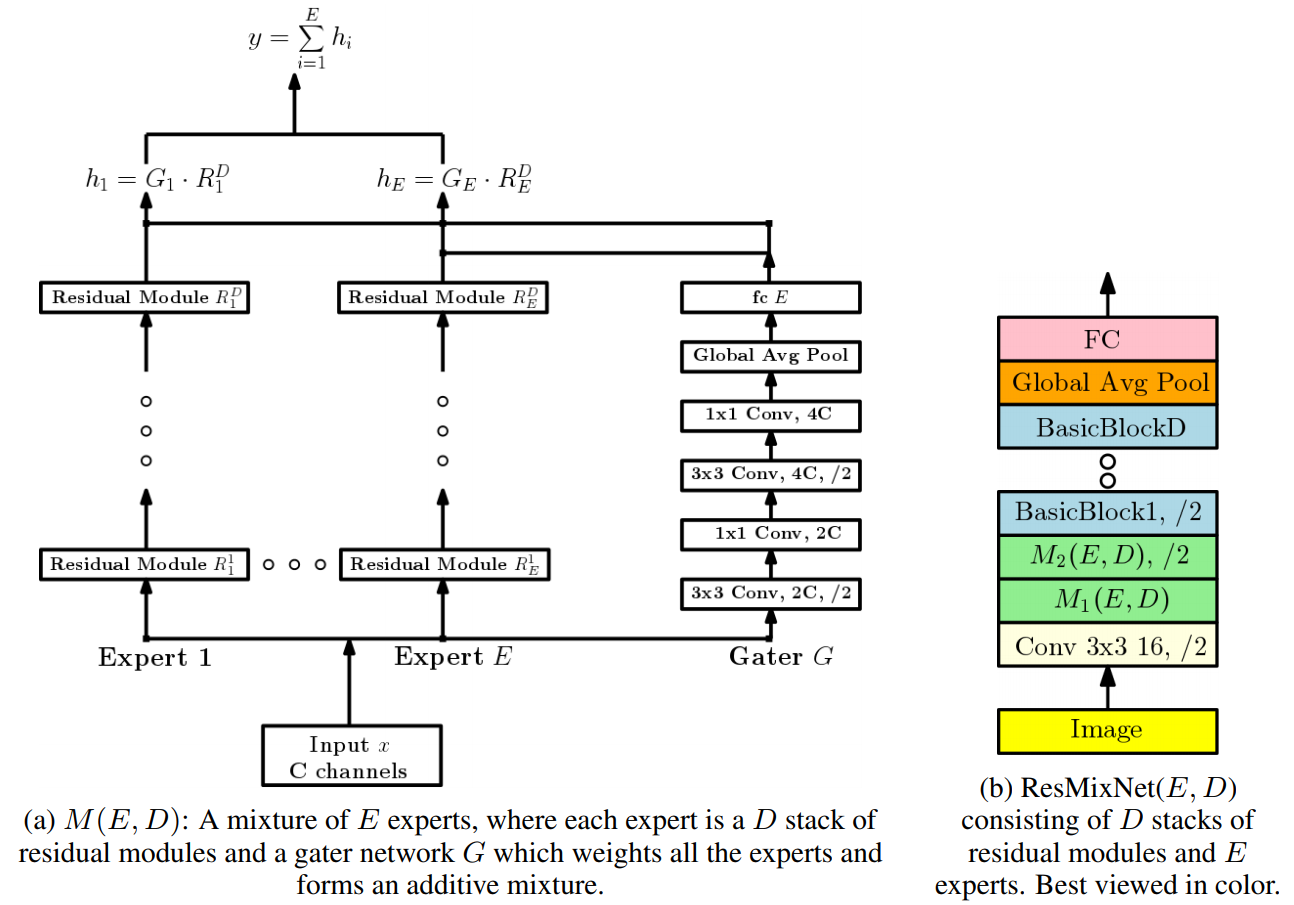
The reason former CNN models are poor at invariant reasoning is interference problem that learning each pattern interfere with each other while a model try to learn many patterns. To minimize this problem, this paper suggest mixture of experts architecture(MoE). MoE architecture consists of two parts: Individual expert networks(E_1, ... E_n) and Gater network(G) that weight the output of each expert network.
y = \sum_{i=1}^E G[i]E_iIn this paper, each expert network consists of multiple residual blocks and the architecture is called Residual Mixture Network(ResMixNet).
So?
This paper suggested two tasks to test invariant relational reasoning. First is MNIST Parity dataset which is to predict the parity(both even or both odd) of a pair of numbers in a image. Second is colorized Pentomino dataset which is to learn whether all the Pentomino sprites in an image belong to the same class. ResMixNet achieved the best result on both of these tasks compared to traditional CNN models.
Critic
Modularity Seems quite naive. There should be further development.
