Resilient Distributed Datasets: A Fault-Tolerant Abstraction for In-Memory Cluster Computing
Summary
Resilient Distributed Datasets(RDD) is a distributed memory abstraction to perform in-memory computations of large clusters. While many data-processing algorithms are applied to data iteratively, the reuse of intermediate results are rarely exploited. To enable in-memory processing with fault-tolerence, RDD provide an interface based on coarse-grained transformation while logging the transformations in lineage. RDDs is implemented in a system called Spark. Datasets from stable storage go through transfomations such as map, filter and join from RDDs to RDDs. Lineage keep tracks of this transformation to recover from error. Users can choose to persist data for later reuse or partition the data with key values. 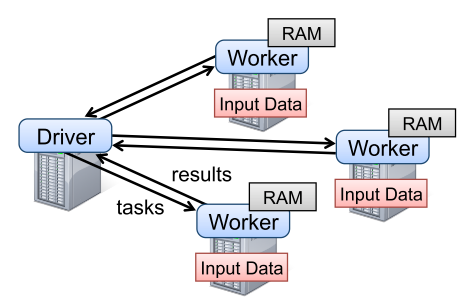 The programming language of Spark is based on Scala. From driver, driver program connects a cluster of workers. Programmers define RDDs and perform several transformations. Then, actions such as count, collect and save are called to perform all the transformation with actions. They can choose to persist the data for later use.
The programming language of Spark is based on Scala. From driver, driver program connects a cluster of workers. Programmers define RDDs and perform several transformations. Then, actions such as count, collect and save are called to perform all the transformation with actions. They can choose to persist the data for later use. 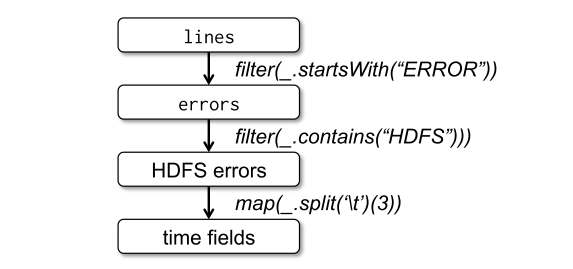
Strengths
Very fast in-memory processing especially useful in machine learning.
Weaknesses
Not suitable for fine-grained operations.
New things I learned
The fact that Spark is extremely useful in machine learning and quite intuitive to use.
Discussion topics
Can fine-grained operations be supported by Spark?
