The Hadoop Distributed File System
Summary
Hadoop Distributed File System(HDFS) construct file system in cluster level. Huge amount of data are stored in distributed servers and enable users to access with high bandwith. Just like UNIX file system, HDFS keep metadata for data it stores. A dedicated server that stores metadata is called NameNode, and other servers that store application data is called DataNodes. All servers communicate through TCP-based protocol. To enable high bandwith and quick access, HDFS replicate data on multiple DataNodes(usually 3). The metadata that stores the structure of HDFS is called image. To ensure security, the persistent state of the image is recorded as a checkpoint. Also, the changes after a checkpoint is also stored as journal. Image can be restored with the checkpoint and the journal. To improve security, BackupNode that stores state of the image in memory and snapshot that provides roll-out in case of version collision are introduced. 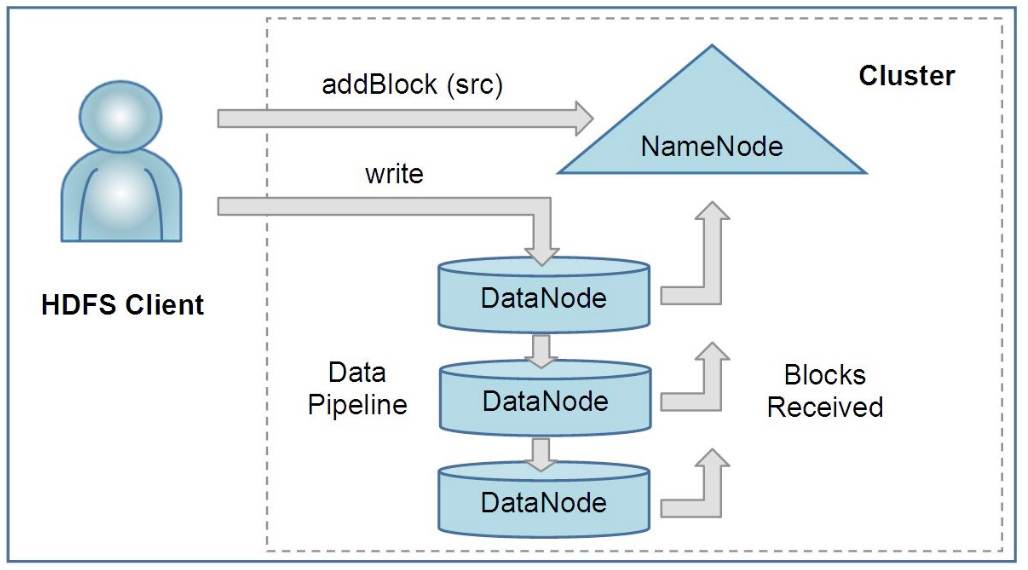 NameNode and DataNodes communicate through heartbeat. NameNode provides the nearest DataNode when HDFS read data. Writing is tricky since same data are replicated in several DataNodes. When writing occurs, HDFS pipelines DataNodes to update the data sequentially.
NameNode and DataNodes communicate through heartbeat. NameNode provides the nearest DataNode when HDFS read data. Writing is tricky since same data are replicated in several DataNodes. When writing occurs, HDFS pipelines DataNodes to update the data sequentially.
Strengths
Huge amount of data can be stored in many servers.
Weaknesses
Replicated data would require much more storage size.
New things I learned
How data are managed in a cluster level.
Discussion topics
What would be the appropriate algorithm to decide the number of replication of data?
