A Two-Step Disentanglement Method
WHY?
This paper wanted to disentangle the label related and label unrelated information from data. The model of this paper is simpler and more effective than that of Disentangling Factors of Variation in Deep Representations Using Adversarial Training.
WHAT?
Let S represents labeled information and Z represents the rest. 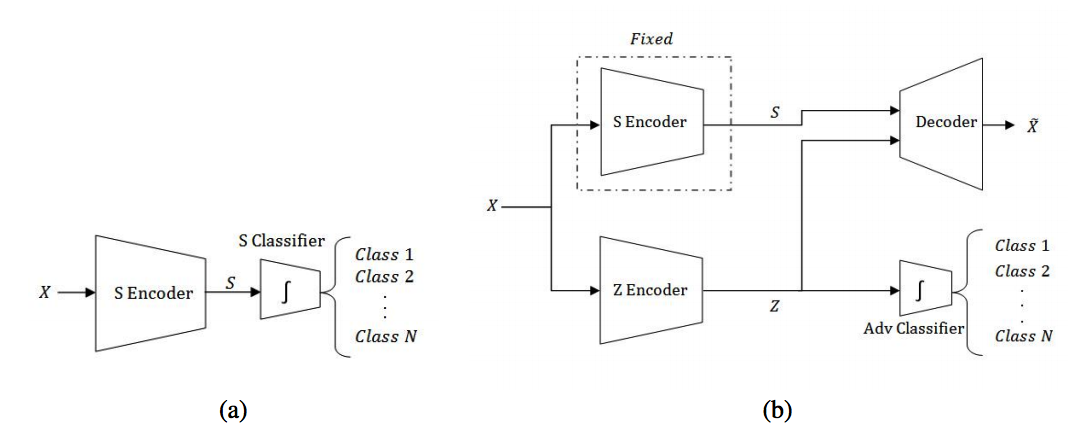 The first step is to train the S-encoder with a classifier to classify the label so that S-encoder can extract the information that are related to label. In the second step, while the S-encoder is kept fixed, the output of S-encoder and that of Z-encoder are used together for reconstruction. To make sure that Z-encoder does not contain any information of label, another adversarial classifier are train to classify the output of Z-encoder. Z-encoder and decoder is trained together to minimize the loss of reconstruction and the negative of the loss of classifier (maximize the loss of classifier:
The first step is to train the S-encoder with a classifier to classify the label so that S-encoder can extract the information that are related to label. In the second step, while the S-encoder is kept fixed, the output of S-encoder and that of Z-encoder are used together for reconstruction. To make sure that Z-encoder does not contain any information of label, another adversarial classifier are train to classify the output of Z-encoder. Z-encoder and decoder is trained together to minimize the loss of reconstruction and the negative of the loss of classifier (maximize the loss of classifier: L_{rec} - \lambda * L_{adv}).
So?
This model showed to clearly disentangle the distribution of unlabeled data while the model of Disentangling Factors of Variation in Deep Representations Using Adversarial Training showed some entanglement in Z due to its Gaussian distribution assumption. This model showed clean disentanglement in MNIST, Sprites and NORB. Interestingly, this paper used the model to financial data to disentangle the information of market from the price of a specific stock.
Critic
Simple but clean idea to disentangle the labeled information.
