Massively Parallel Methods for Deep Reinforcement Learning
WHY?
A single agent usually takes too long to train.
WHAT?
Stacking experience with multiple agents would boost-up the speed of training. In addition, parralell gradient calculation can be used if multiple GPUs are available. This paper called this framework Gorila(General Reinforcement Learning Architecture).
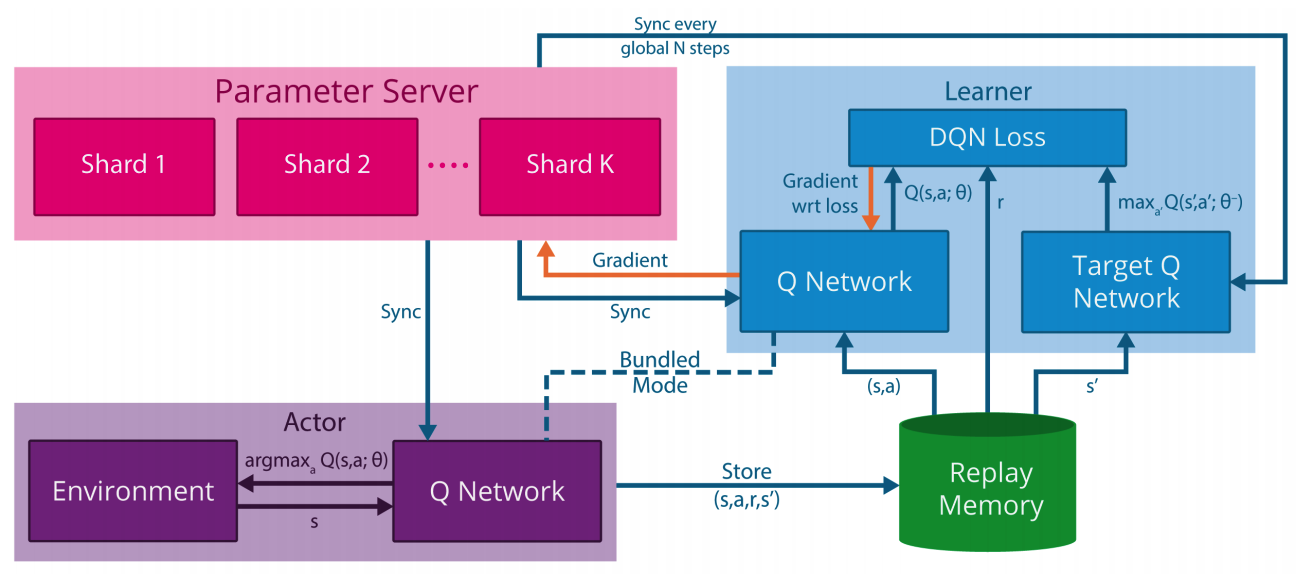 Gorilla consists of 4 parts: Actors, Experience replay memory(Database), Learner, and parameter server. Actors interact with the environment selecting action with given model and gather experience to store in replay memory. Experience replay memory can take 2 form: local replay memory and global replay memory. Local replay memory stores the experience of actors separately and global replay memory stores them all together. Learner sample from replay memory and calculate the gradient of parameters of given models. Parameter server stores the parameters of the model and multiple servers can store split parameters. This update the parameter with the gradient from learners and provide newest model to actors and learners. Algorithm is as follows.
Gorilla consists of 4 parts: Actors, Experience replay memory(Database), Learner, and parameter server. Actors interact with the environment selecting action with given model and gather experience to store in replay memory. Experience replay memory can take 2 form: local replay memory and global replay memory. Local replay memory stores the experience of actors separately and global replay memory stores them all together. Learner sample from replay memory and calculate the gradient of parameters of given models. Parameter server stores the parameters of the model and multiple servers can store split parameters. This update the parameter with the gradient from learners and provide newest model to actors and learners. Algorithm is as follows. 
So?
The agents were tested with the average of 30 episodes upto 18000frames(5mins) with both normal inital point and human picked initial point. Agent trained with Gorila framwork with 100 actors and learners were trained much faster.
Critic
It would be beneficial if the paper suggest the method for efficient communication among the parts.
